by Vaibhavi M.
5 minutes
Pharma Manufacturing Processes Explained: From Batch Manufacturing to Digital Shift In 2025
This article highlights the three most common pharmaceutical manufacturing processes: chemical synthesis, fermentation, and bioprocessing.

The pharmaceutical industry is among the largest industries in the world with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% between 2024 and 2031. The growth of this industry depends heavily on developing new medications and products. A huge part of this growth is attributed to pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
Efficient drug manufacturing and an optimized pharmaceutical manufacturing process are crucial to maintain high standards and meet global demand.
It is necessary to understand pharmaceutical manufacturing processes to ensure drug safety and efficacy, ensure compliance with regulatory standards, foster innovation within the company, effectively manage crises, and fulfil ethical responsibilities.
Leveraging big data in pharmacovigilance also plays a critical role in identifying risks early and enhancing drug safety. People working in the pharmaceutical industry, both directly and indirectly, should especially understand pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
This article highlights the three most common pharmaceutical manufacturing processes: chemical synthesis, fermentation, and bioprocessing.
Modern manufacturing of pharmaceuticals integrates digital tools to enhance production in pharmaceutical industry and improve efficiency in the drugs manufacturing process.
The manufacturing process in pharmaceutical industry
We'll go over each of the important steps involved in the production of pharmaceuticals below:
- Development and research (R&D): Scientists create novel medications, test them, and run preliminary studies to determine their effectiveness.
- Formulation: To create a stable, potent product, the API’s in the medication are mixed with additional excipients.
- Production: The drug is manufactured in bulk quantities according to precise documented protocols to guarantee uniformity and quality.
- Quality control: To ensure its safety, effectiveness, and quality, every batchundergoesh a thorough testing process.
- Distribution and packaging: The finished product is sent to pharmacies, medical facilities, and healthcare professionals across various markets after being packaged into the appropriate dosage form.
Understanding pharmaceutical industry production and integrating advanced systems into pharmaceuticals manufacturing process ensures quality and consistency in manufacturing of drug.
Batch Manufacturing v/s Continuous Manufacturing
The pharmaceutical industry is evolving from the conventional batch manufacturing process to the more modern continuous manufacturing approach. The need for increased efficiency, reduced production times, and enhanced product quality drives this shifty.
Transitioning from batch to continuous drugs manufacturing process enhances the pharmaceutical manufacturing process, streamlining production in pharmaceutical industry.
Continuous pharmaceutical manufacturing has grown in popularity in recent years as companies explore batch-to-continuous manufacturing for greater efficiency and scalability.
Although batch processing and continuous flow manufacturing are fantastic tools in the pharmaceutical world, bot haver pros and cons for pharmaceutical manufacturers and consumers.
Batch Manufaturing Process
So far, the production of pharmaceuticals has been using batch manufacturing. In this approach, drugs are produced in discrete steps: raw materials are processed in separate batches, each undergoing its own operations. The flexible approach also caters for small-scale production.
Advantages of Batch Manufacturing:
The advantages make batch manufacturing especially suitable for smaller-scale production, clinical trials, or products with fluctuating demand.
- Lower Initial Set-Up Costs - Batch production is less costly to invest up front than continuous systems; therefore, are more economical to start.
- Flexibility and Customisation - Each batch’s composition can be customized, thus drug companies can change the composition of a drug in various ways, including formulation, amount, or packaging in relation to special needs or markets.
- Ideal for Certain Formulations - Some products or ingredients must be subjected to batch processing because of their chemical characteristics making this method the only viable option.
- Responsive to Market Demand - Companies can manufacture fixed amounts of a drug, take a break and switch their attention according to market requirements, avoiding overproduction and wastage.
Challenges of Batch Manufacturing:
- Time-Consuming: Each of the batches needs setup, processing, and cleaning, which takes more time to produce them.
- Inconsistencies: Batch variation can exist, affecting product quality.
- Resource Intensive: Frequent equipment cleaning and validation require high resource consumption
Batch methods are essential in drug manufacturing, especially for smaller-scale production in pharmaceutical industry, maintaining compliance in pharmaceutical industry production.
Continuous Manufacturing Process
Continuous manufacturing is a shift in paradigm, in which raw materials are continuously entered in the production process, while the final product is produced without a break. This approach combines the production process into one continuous flow.
Advantages of Continuous Manufacturing:
- Efficiency: Time for production is reduced, while not requiring batch-wise processing.
- Consistency: Provides unified product quality, based on the steady-state operations.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the costs of the operations by optimising downtime and cutting down on resources.
- Scalability: Easier to take the production to greater levels without too many changes to the process.
Challenges of Continuous Manufacturing (CM):
- Regulatory Challenges - Lack of globally harmonised guidelines complicates global approval. Fear of regulatory delays remains a barrier despite growing support from the FDA and EMA.
- High Initial Investment - Continuous manufacturing requires expensive PAT tools and automation. Difficult for companies, especially those producing generics, to switch from already-approved batch setups.
- Quality & Safety Concerns - Material traceability is complex due to continuous flow, and advanced control systems are essential to maintain product quality and safety.
- Equipment & Technology Limitations - Limited availability of equipment, especially for small or mid-sized manufacturers. Late pharma involvement in technology development has slowed innovation.
- Skills Gap - Shortage of trained professionals in continuous manufacturing and advanced statistical/data systems. Shift toward automation reduces manual jobs but creates demand for high-skill roles.
- Dosage Form Limitations- Most CM-approved drugs are oral solid doses also known as conventional drugs. Biopharmaceuticals and complex dosage forms (e.g., vaccines) pose greater technical challenges.
Continuous manufacturing enhances pharmaceutical manufacturing process and modern drugs manufacturing process, allowing reliable manufacturing of pharmaceuticals at scale.
API v/s Formulation Manufacturing
Understanding the journey from API to Final formulation helps us to understand the science and precision behind every pill, syrup, or injection. It’s a combination of chemistry, engineering, and patient-centric design all working together to deliver healthcare in its most accessible form.
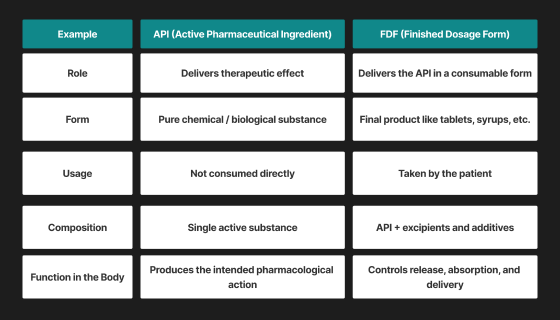
What is an API?
API is an abbreviation for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient, which is the essential medical element in any drug. It’s the chemical or biological agent that actually provides the therapeutic effect that interacts with the body to cause the desired medical effect.
From reducing blood pressure, fighting infections, to relieving pain, it is the API that will get the job done. Although APIs are strong, they do not get consumed in the true sense; they have to be combined with other elements to make the ultimate medicine.
APIs can be created in different ways:
- Chemically synthesised in labs through complex reactions,
- Biotechnologically engineered using living organisms, or
- Extracted from natural sources such as plants or minerals.
What is an FDF?
FDF is an abbreviation for finished dosage form, which is the ultimate form of the medicine, for example, tablets, capsules, syrups or injectables that a patient consumes.
The API is part of FDF along with other such ingredients as binders, fillers, preservatives, and flavouring agents known as excipients. In other words, formulation refers to the conversion of the raw, active ingredients to an available, safe and effective medicine.
These excipients don’t have any medicinal effect on their own, but are essential for:
- Ensuring the stability of the drug,
- Controlling how and where the API is released in the body,
- Improving taste, texture, or shelf-life, and
- Making the medicine easier to consume.
Proper pharmaceutical manufacturing process ensures APIs and FDFs maintain consistent quality in production in pharmaceutical industry.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing process overview of API and FDF
API Manufacturing Process
- Raw Material Procurement – Starting materials and reagents are sourced.
- Chemical Synthesis or Biotech Processing – APIs are created through complex multi-step reactions or fermentation.
- Purification – The API is separated from by-products and purified.
- Crystallisation/Drying – The API is converted into a stable form, often through drying and crystallisation.
- Quality Control & Testing – The final API is tested for purity, potency, and consistency using advanced quality control technologies to ensure product safety and efficacy.
FDF Manufacturing Process
- Formulation Design – API is combined with suitable excipients depending on the dosage form (tablet, capsule, liquid, etc.).
- Mixing/Granulation – Ingredients are blended uniformly; granulation may be done for better tablet formation.
- Compression/Encapsulation – For solid forms, the blend is compressed into tablets or filled into capsules.
- Coating/Finishing – Tablets may be coated for controlled release or taste masking.
- Packaging & Labelling – Final products are packed and labelled for distribution.
- Quality Assurance – Final testing is done to confirm dosage accuracy, stability, and safety.
Optimized drugs manufacturing process improves pharmaceutical industry production, ensuring high-quality drug manufacturing.
Digital Transformation in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Digital transformation in pharma – what is it?
Digital transformation in the pharmaceutical world is more than just swapping paper for screens. Yes, it starts with digitising data and documents, but it goes deeper; it's about rethinking how work gets done.
Yes, it begins with the digitisation of data and documents, but it goes further; it’s about rethinking how work gets done. That’s automation of operations, coupling isolated systems, and leveraging data at all levels of the decision-making process from the lab to the production floor.
Though almost every industry is being transformed by digital transformation, pharma has been slow for pharma to adopt. Much of that comes down to stringent compliance needs and the need to ensure patient safety, and to protect proprietary research and intellectual property.
With the pressure mounting to stay ahead, pharma companies are now warming up to digital transformation in pharma to modernise operations, cut the regulatory hassles and become more agile to market demands.
Digital tools enhance pharmaceutical manufacturing process and improve production in pharmaceutical industry, while streamlining drug manufacturing and drugs manufacturing process operations.
Why Digital Transformation in Pharma Is Important
In other words, Digital transformation in pharmaceuticals is all about getting things done faster, safer and smarter. With connected technologies, companies can access massive improvements in building and releasing drugs.
It may be a response to several needs such as creating a new production line to replace an ageing production line, preparing for tougher regulation, addressing workforce gaps, or just plain increasing profits.
Core Objectives of Digital Transformation in the Pharmaceutical Industry In 2025
Process Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks and use real-time data to streamline manufacturing and lab operations. The goal is to make processes faster, more consistent, and less prone to error.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Turn raw data into actionable insights. When systems talk to each other and share data, managers and teams can make quicker, more informed decisions.
Product Quality: Reduce defects, speed up batch changeovers, and improve CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Actions) processes. Digital systems help ensure quality is built into every step, not just checked at the end.
Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory agencies are now supporting digital advancements. Smart systems can simplify compliance by automating documentation, ensuring traceability, and aligning with evolving guidelines.
Flexibility & Agility: Whether it’s a supply chain disruption or a sudden shift in demand, digital systems make it easier to pivot and respond to change quickly.
Productivity: Boost throughput and reduce downtime by focusing human efforts on value-added work. Automation takes care of the repetitive, freeing teams for innovation and oversight.
Risk Reduction: From preventing product recalls to minimising operational disruptions, digital tools help identify and manage risks before they turn into bigger issues.
Digitally enabled pharmaceutical manufacturing process ensures better quality, faster drug manufacturing, and more reliable pharmaceutical industry production outcomes.
Conclusion
In 2025, pharmaceutical manufacturing is rapidly evolving, driven by innovation, digital transformation, and a need for greater efficiency. From APIs to finished formulations, the manufacturing process in the pharmaceutical industry is being reimagined to ensure safer, faster, and more reliable outcomes.
The shift from batch to continuous production is streamlining the pharmaceutical drug production process, while automation and data integration are transforming the pharmaceutical production system.
As companies modernise their operations, understanding the full pharmaceutical manufacturing process overview is crucial to staying competitive and compliant. Ultimately, smarter manufacturing in the pharmaceutical industry means better healthcare delivery worldwide.
FAQs
Q1. What is continuous manufacturing in pharma?
Continuous manufacturing is a modern pharmaceutical production method where raw materials are continuously fed into the process, and finished products are consistently produced in a streamlined flow. It improves efficiency, reduces waste, and ensures consistent product quality compared to traditional batch manufacturing.
Q2. What is the difference between API and formulation manufacturing?
API Manufacturing: Involves creating the active ingredient that provides the drug’s therapeutic effect.
Formulation Manufacturing: Involves combining the API with excipients to produce the final consumable form, like tablets, capsules, or syrups
Q3. What are some common challenges in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes?
Regulatory compliance and quality control are common challenges for most companies. Companies have to regularly review their manufacturing processes to ensure they are compliant and produce high-purity products.
Q4. How are manufacturing processes divided?
Pharmaceutical manufacturing processes are divided into batch processing (products are synthesised in batches) and continuous processing (products are synthesised using a continuous, never-ending process).




