by Mrudula Kulkarni
6 minutes
Process Validation in Pharma Manufacturing: New Standards for Quality in 2025
Pharma validation ensures manufacturing systems, processes, and equipment produce high-quality, compliant products.

Process validation in pharmaceutical manufacturing is a detailed procedure to ensure the manufacturing process consistently produces high-quality products. Validation processes are generally performed by validation teams such as quality assurance teams.
They are usually performed before releasing new products, changing existing products, integrating new processes or equipment, or for quality control/assurance of existing methods.
Validation processes are an integral part of the manufacturing process, and every company has to design and integrate them to meet the standards.
However, despite being a necessity, many must understand the importance of validation in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Therefore, here’s an overview highlighting everything you need to know about validation in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
What is the role of validation processes in pharmaceutical manufacturing?
There are several advantages of implementing validation processes in pharmaceutical manufacturing, such as ensuring quality and compliance. Here’s how successfully validation can be advantageous for pharmaceutical companies:
Enhanced product quality
The primary advantage of validation processes is that they ensure the production line manufactures products with consistent quality and up to the pre-determined quality standards. Consequently, the pharmaceutical company can sell consistent, high-value drugs that meet the market standards.
Regulatory compliance
Pharmaceutical manufacturing processes need to meet strict guidelines and standards decided by regulatory agencies. Validation processes ensure these guidelines are consistently met. Furthermore, it allows compliance lapses to be identified.
Risk mitigation
Frequent quality validation processes can be used to identify potential risks in manufacturing processes, such as equipment defects. This can reduce the drop in product quality, which may result in product recalls and batch failures.
Compliance with GMPs
Process validation allows pharmaceutical manufacturers to comply with good manufacturing practices (GMPs). GMPs in pharmaceutical manufacturing are critical for maintaining the safety and integrity of products. These also hinder market entry, and non-compliance with GMPs may result in product recalls.
Faster market access
Process validation is a prerequisite for market entry and maintaining access to the market (i.e., to continue selling the product). The development of validation processes shows regulators and other stakeholders that the developed methods can produce high-quality products consistently and efficiently.
Considering these advantages, you may wonder: How is process validation implemented in the industry? Well, it’s not very complex and generally involves only three stages!
What are the three stages of process validation?
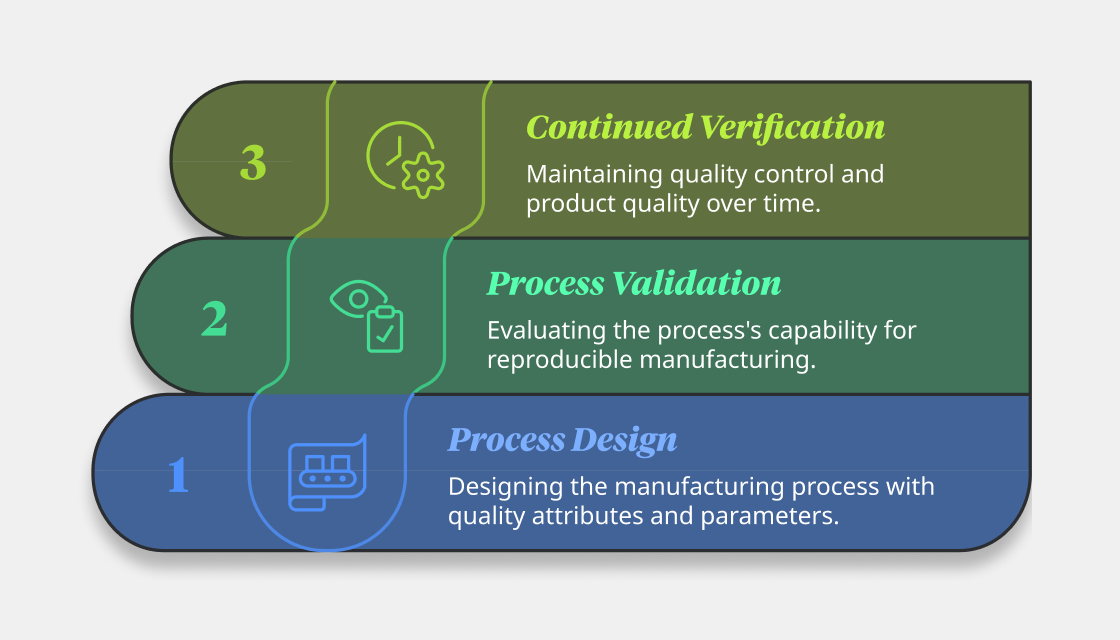
Stage 1: Process design
In this stage, the commercial manufacturing process is designed end-to-end based on the production requirement, scale-up opportunities, and inputs from manufacturing teams. Herein, the crucial quality attributes of the product are defined, and the process parameters the affect these quality attributes are identified.
Stage 2: Process validation
In the second stage, the designed process’s capability for reproducible manufacturing is evaluated. First, equipment and utilities are selected and validated. Then, process performance is qualified. Finally, the consistency and reproducibility of the process is evaluated.
Stage 3: Continued verification
In the final stage, the goal is to maintain quality control and product quality over time. It involves the continuous monitoring of manufacturing processes, undertaking risk assessments, designing new control strategies, and taking corrective/preventative actions to prevent deviations—key aspects of pharma manufacturing quality control.
These stages help you develop a validated process for any operation. Now, naturally, the next question that arises is: which key validation processes must be integrated? Here’s a simple answer.
Which are the critical validation processes used in pharmaceutical manufacturing?
Process validation
Process validation ensures the manufacturing process operates according to necessary standards and requirements. During this validation, data is collected from the process design stage to the commercial production stage. Validators also use historical data and operational data to validate information.
Equipment validation
Equipment validation is integral to ensure that product quality remains consistently high. Generally, equipment validation is divided into three:
- Installation qualification (IQ): IQ aims to verify whether the equipment is installed according to appropriate guidelines. For example, some instruments may require sunlight, and others may need frequent air flow – all of which must be verified after installation.
- Operational qualification (OQ): OQ determines whether the equipment operates as intended. During OQ, validators check equipment parameters (e.g., temperature, noise level, cleanliness, and accuracy.) to determine whether they meet necessary standards.
- Performance qualification (PQ): PQ aims to verify the performance of the equipment under production conditions. Validators usually take data during operation/manufacturing.
Analytical method validation
Analytical methods are used to test product quality and consistency. Analytical method validation studies whether these analytical methods are reproducible and reliable. Validators study analytical methods' accuracy, precision, detection limit, range, and more.
To support these validations, many pharmaceutical companies are now adopting advanced pharma quality control technologies that enhance analytical precision and process efficiency.
Cleaning validation
Pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment must be thoroughly and frequently cleaned to ensure no contamination. Pharmaceutical companies usually create strict cleaning schedules and protocols. Cleaning validation is the validation of these cleaning schedules and protocols.
Validators assess whether the protocols can efficiently remove residue. They also validate the levels of cleaning agents, cleaning time, cleaning frequency, and cleaning instruments used.
Computer system validation
Integrating as many technologies as possible is necessary to make manufacturing simple and efficient. However, computer systems often control these technologies, equipment, and instruments. These systems also need to be validated.
This generally includes assessment of data measurement accuracy, data analytics accuracy, and more. It also assesses how, where, and why data is stored, used, and analysed.
Facility Validation
Last but most important is facility validation. Facility validation is performed to ensure the manufacturing facility meets the required standards. Validators assess the humidity, contamination control, temperature, light intensity, and other factors affecting product quality. Facility validation is usually performed periodically after the facility is set up.
In recent times, because most companies are shifting from batch manufacturing to continuous manufacturing, new process validation approaches have been developed. Here’s a quick snapshot of upcoming process validation approaches.
New validation approaches for continuous manufacturing
- Process analytical technology (PAT): PAT such as spectroscopy, particle size analyzers, and low sensors are being integrated to monitor critical quality attributes in real-time. The use of these ensures real-time measurements to identify quality lapses.
- Residence time distribution (RTD) modeling: RTD models determine which material creates the risk of process deviation. These models define how materials move through the process, increasing traceability, defining boundaries, and identifying disturbances & their downstream impacts.
- Integrated control technologies: These often include feedback loops and feedforward control, where, when a problem is identified, the feedback is immediately sent upstream so that the process can be rapidly adapted. These often depend on alarms, sensors, and rapid analytical technologies.
Many companies often implement risk-based process validation strategies. Here’s a brief explanation of what these are:
Risk-based validation strategies
Risk-based process validation focuses on identifying, assessing and mitigating risks to product quality throughout the product cycle. The core principles of these strategies are:
- Prioritize the validation of critical quality attributes and the corresponding process parameters.
- Take a lifecycle-based approach rather than a one-point approach, i.e., validation should be done throughout the process not only at points where risk arises.
- Use risk management tools to define design space and control strategies, which will help rapidly solve future problems.
Here’s what it looks like in the real world:
- Identify potential failure modes and quality risks using checklists or process maps.
- Assess the severity, detectability, and probability of each risk.
- Establish control, monitoring and mitigation strategies, including acceptable limits and intervention steps.
- Document the rationale behind decisions to ensure it’s thoroughly communicated among the team.
- Perform periodic assessments as more data becomes available to identify more risks or whether the existing risks are sufficiently handled.
Challenges facing validation in pharmaceutical manufacturing
High costs
The implementation of validation processes is expensive. Companies have to hire experts and train staff to ensure they can perform the necessary procedures. They may have to hire consultants or outsource validation, both of which are expensive.
Shifting guidelines
Regulatory guidelines constantly change, and validation processes must be updated regularly to ensure compliance. Keeping up with evolving guidelines from multiple regulatory bodies is daunting.
Furthermore, different regulatory bodies and governments have different policies, increasing complexity. These challenges are commonly encountered in the realm of pharma regulatory affairs, requiring teams to stay constantly updated and adaptable.
Resource requirement
For validation to be effective, it must be performed by skilled personnel with expertise in quality assurance, regulatory compliance, and engineering. Companies must constantly upskill and train their staff on new guidelines and requirements.
Conclusion
Validation in pharmaceutical manufacturing is an integral process that ensures quality and compliance. It allows pharmaceutical companies to manufacture good-quality products consistently. There are six types of validation: process, equipment, analytical methods, cleaning, computer system, and facility validation.
However, performing these validations takes time and effort, primarily because many resources are required, and guidelines are constantly changing. Pharmaceutical companies have made excellent strides in integrating these validations despite these challenges.
FAQs
1. How often are validation processes conducted?
Validation is performed several times: when the facility is established, during process integration, during integration of new equipment, and periodically throughout operation.
2. How is validation performed?
Validation is often performed using standard operating procedures, which the pharmaceutical company establishes according to regulatory guidelines and GMPs.
3. Is validation the same as verification in pharmaceutical manufacturing?
No. Validation ensures a process performs consistently, whereas verification confirms whether specific requirements are met.
4. What are the stages of process validation?
Process validation usually contains three major steps: process design, process quantification, and continued process verification. Together, the ensure the process continuously affords products that meet the specific standards.
5. How continuous manufacturing changes validation?
Continuous manufacturing changes batch-wise validation to continuous step-wise validation. Hence, the process is analyzed and validated at (seemingly) random or predefined instances instead of in batches.




